We heavily rely on external storage devices like hard drives or SSDs for storing & backing up data. These devices are suitable for a limited amount of data. But when it comes to storing huge amounts of data running in 10s of TBs, users prefer RAID arrays or NAS drives over individual storage drives. These storage solutions not only cater to individual needs but also pose as efficient enterprise data storage solutions.
However, just like any other storage device, these two have various advantages, disadvantages, and differences. Let’s read further to find out what makes these two storage solutions different from each other and how users can benefit from them.
What is RAID?
RAID, or Redundant array of independent Drives/Disks, is a set of multiple hard drives or SSDs configured in a way to act as one logical unit. A RAID setup is primarily used to improve read/write performance, enhance data security against unexpected data losses due to drive failure or other reasons, and increase storage capacity.
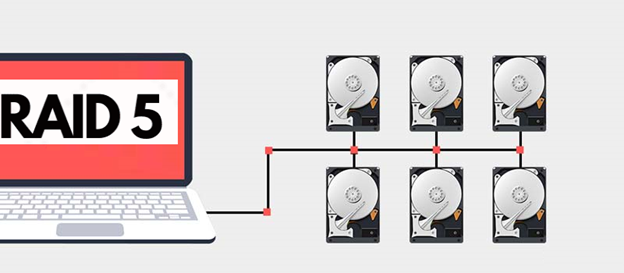
A RAID array consists of a number of individual storage drives configured at a specific level. There are numerous RAID levels but the most common ones are RAID 0, RAID 1, RAID 5, and RAID 10. All RAID levels work on data storage, security, and availability. Every level works on one or more data storage mechanisms like mirroring, striping & parity. Advanced RAID levels or Nested RAID arrays (RAID 10, RAID 50, etc.) use a combination of these mechanisms to increase data security, availability and reliability.
A major aspect of using a RAID array is redundancy. All RAID levels except for RAID 0 provide some kind of redundancy. This redundancy means the amount of disk failures a RAID setup can endure. However, with the right RAID recovery software, one can easily recover data from a RAID setup without much hassle.
What is NAS?

NAS, or Network Attached Storage, is a file-level data storage solution that supports file sharing on a network. It works as a single or centralized point for people to store, share and access data over a network. Unlike a RAID server, NAS allows multiple people to access data at any given time. Therefore, it serves as a good data storage option for enterprises to store data in a secure and centralized place.
A significant reason why NAS is a preferred storage solution over RAID is its scalability and flexibility. NAS acts as a private cloud storage, which is faster, less expensive to build, and always accessible.
Though NAS is a completely different data storage solution, in most cases, it consists of a RAID array connected over a network. This not only increases the availability of data but also makes it more secure. However, there is always a possibility of a NAS failing due to drive failures or other reasons. In such a situation, one can employ an advanced NAS recovery software for recovering data from a failed NAS.
NAS Vs. RAID: Which is Better?
NAS and RAID are separate data storage technologies that offer numerous benefits. However, they both can work together or separately, as individual storage devices. Tabulated below are a few key distinctions that can help you make a better decision.
|
RAID |
NAS |
|
RAID is a combination of multiple disks that act as a single data storage unit. |
NAS or Network Attached Storage is a data storage mechanism that uses a network to support file sharing. |
|
RAID uses HDDs and SSDs. |
NAS uses a RAID array to store data. |
|
Provides fault tolerance to avoid data loss. |
Provides a centralized location to create a master backup for data on local machines. |
|
It can be internal or external. |
It is external. |
|
It is independent of LAN. |
It is dependent on LAN. |
|
Performance is governed by the quality of drives, type of RAID controller, and selected RAID level. |
Performance is governed by Processor, RAM, and the number of drives used. |
Which one to choose?
With an endless amount of information surrounding RAID and NAS, it becomes overwhelming for any user to make the right decision. Therefore, to choose the right data storage type, first, you need to have clarity of intent.
In simpler words, if you are looking for a centralized data storage unit that can be accessed 24×7 by authorized users connected via a shared network, then you can opt for a NAS. It is simple to configure and easy to use. And if you run a small or medium-sized business, then having a NAS setup would surely bring data storage costs down to some degree.
And even if you intend to make a personal data storage server for your home, you can either go for NAS enclosures available in the market or build a Linux-based NAS using custom parts. You can also configure the drives as a RAID for increasing data availability, performance, and redundancy.
If you are looking for something that can fit inside your laptop or desktop computer, then RAID is a good option. You can attach multiple HDDs/SSDs (depending upon the SATA connectors on your motherboard) and configure a RAID.
For this, you can use Windows’ in-built Storage Spaces feature to easily setup a RAID. Setting up a RAID array on a Windows computer using Storage Spaces is very simple.
Closing Statement
Both RAID and NAS are specialized data storage solutions that serve their intended purpose. The differences between the two can perplex any new user. Hence, to simplify things, we created this guide to highlight the key differences between them.
The ball is now in your court and the decision primarily depends upon the usage and your intent, and of course, the budget.
Regardless of your choice, always maintain backups and use a dedicated RAID/NAS recovery software in case things go south and you lose some data.